China Net/China Development Portal Network News The Yangtze River is the longest river in China, the third longest river in the world, the national strategic water source, and the golden waterway with the largest freight volume in the world. The Yangtze River plays an irreplaceable role in maintaining China’s ecological and water security. Relying on the golden waterway of the Yangtze River, the construction of the Yangtze River Economic Belt is a major regional development strategy of the country in the new period, and it is also the main axis to form the national "one body and two wings" development and opening up pattern. In January 2016, General Secretary of the Supreme Leader stressed at the symposium on promoting the development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in Chongqing: "The Yangtze River has a unique ecosystem and is an important ecological treasure house in China. At present and for a long time to come, it is necessary to put the restoration of the ecological environment of the Yangtze River in an overwhelming position, work together for great protection and not engage in great development. " This has set the general tone of ecological priority and green development for the development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
The Yangtze River Economic Belt has a prominent ecological position and great development potential. However, due to the cumulative effect of long-term high-intensity development and the lack of scientific spatial development control, the ecological environment situation of the Yangtze River Economic Belt is grim. Not only the water environment and water ecological problems of the Yangtze River are becoming more and more serious, but also the main drinking water sources along the local shore of the main stream are staggered with dangerous goods docks and sewage outlets, the pollution zone along the shore is expanding, the water environment level is declining, the species and quantity of aquatic organisms are decreasing, and many rare species are on the verge of extinction. Moreover, the mountain ecological degradation and geological disasters in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River basin are frequent, the lake wetlands in the middle reaches are shrinking, the relationship between rivers and lakes is tense, and the water environment pollution and lake eutrophication in the lower reaches of the river network are increasing, thus seriously threatening the status of the Yangtze River as a national strategic water source and an important ecological support belt. The Yangtze River Economic Belt has become the fundamental requirement for the country to maintain regional ecological security and improve the level of ecological civilization construction.
This paper is based on the statistical data such as the bulletin of water resources in the Yangtze River basin and the southwest rivers, the bulletin of ecological and environmental monitoring of the Three Gorges Project (1997-2016), the China Statistical Yearbook, the weekly monitoring report of the state-controlled water quality section of China Environmental Monitoring Center (2006-2018), the data of the National Urban Air Quality Daily of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (2015-2019), remote sensing interpretation data at different times, and the data accumulated by historical and long-term special studies. This paper objectively examines the ecological background and basic conditions of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, deeply analyzes the major ecological and environmental problems existing in the development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, and puts forward the overall strategy of "jointly protecting and not developing" in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, for the reference of relevant research and decision makers.
Ecological background and ecological environment problems faced by the development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt
The service value of the Yangtze River ecosystem is irreplaceable, and it is an important strategic water source for the country.
The Yangtze River is an irreplaceable strategic water source and clean energy base. The average annual runoff of the Yangtze River is 9.6×1011 m3, accounting for about 36% of the total fresh water resources in China. It not only meets the production and domestic water needs of about 42% of the population, 38% of grain production and 44% of gross national product (GDP) output, but also alleviates the shortage of urban and rural water resources in North China through inter-basin water transfer, such as the middle route and the eastern route of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project, and becomes an important reliance for the country to cope with the future water resources security. The theoretical reserves of flowing water power in the trunk and branch of the Yangtze River reach 3.05×108 kW, accounting for 40% of the whole country. The hydraulic exploitable capacity is 2.81×108 kW, accounting for 53.4% of the national exploitable capacity. In 2018, the hydropower generation in the Yangtze River Basin was 7.93×1011 kWh, accounting for 66.1% of the country.
The freight volume of the Yangtze River ranks first among inland rivers in the world. In 2019, the Yangtze River trunk ports completed cargo throughput of 3.03 billion tons, container throughput of 18.44 million TEUs, and the Yangtze River trunk ports reached 14 billion-ton ports. In recent years, the main channel of the Yangtze River has been effectively regulated, the deep-water channel of the Yangtze River estuary has been fully completed, and the 12.5 m deep-water channel below Nanjing has been connected, and the 50,000-ton seagoing vessel can reach Nanjing Port with full load.
Fishery in the Yangtze River is irreplaceable. There are 378 species of fish in the Yangtze River system (including lakes), accounting for about 33% of the total freshwater fish in China, ranking first in the fish resources of rivers in China, among which 147 species are endemic, accounting for 42% of the fish species in the Yangtze River. As an important production base of freshwater fish fry in China, the Yangtze River is rich in economic fish such as "four major fishes" (black carp, grass carp, silver carp and bighead carp). Among the 35 main freshwater fish breeding species in China, there are 26 species naturally distributed in the Yangtze River, and there are many precious and high-value breeding species such as Siniperca chuatsi, Silurus meridionalis, Myxocyprinus japonicus, Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Spinibarbus sinensis. The Yangtze River is the most important freshwater fishery germplasm resource bank in China.
The Yangtze River Economic Belt has an important ecological location and is an important gene bank of natural species in the world.
The Yangtze River Economic Belt is rich in natural species resources. Upstream region: It has almost all terrestrial ecosystem types including forest, shrub, grassland, meadow, wetland and alpine tundra, with high net primary productivity (NPP) and rich biodiversity; Ecosystem regulation and support services such as water conservation, soil conservation and biodiversity maintenance are far greater than supply services, but the ecosystem is relatively fragile; Therefore, the protection value of the authenticity and integrity of the ecosystem is high (Figure 1). Middle reaches: Mountain forests, farmland and rivers, lakes and wetlands have a high proportion of ecosystem types and are widely distributed, and ecosystem regulation, support services and supply services are both important. Downstream area: Farmland, rivers, lakes and coastal wetlands are prominent ecosystems.
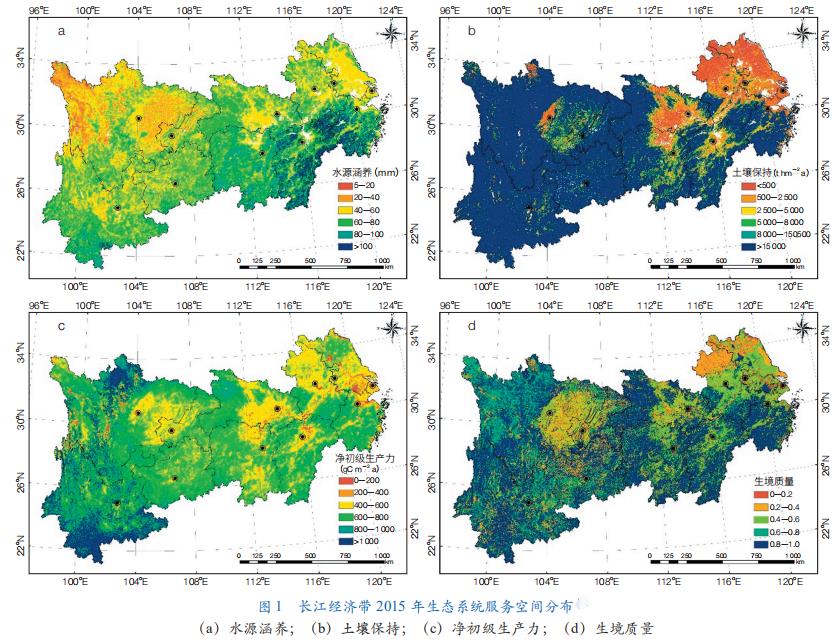
The Yangtze River Economic Belt is located in a moderate position in the north and south, and its superior conditions of light, heat, water and soil ratio have given birth to rich flora and fauna, which has become an important gene bank of natural species in the world and has great biodiversity protection value. There are 1 034 important protected species in the Yangtze River Basin, including 568 species of plants, 142 species of mammals, 168 species of birds, 57 species of amphibians, 85 species of reptiles and 14 species of fish. In addition, as an important habitat and refuge for many rare and endangered aquatic wild animals in China, the Yangtze River has 14 species of national first-and second-class protected aquatic wild animals, including ACIPENSER sinensis, ACIPENSER sinensis and ACIPENSER Changjiang. There are 6 088 species of plants in 208 families, 1 428 genera in the Three Gorges reservoir area alone, 7 037 species in 202 families, 1 476 genera in the middle reaches and 4 259 species in 174 families, 1 180 genera in the lower reaches.
According to the national ecological function zoning, the Yangtze River Economic Belt involves 25 important ecological function zones, accounting for 47.1% of the national total. Among them, there are 8 important water conservation ecological service functional zones in China, including Qinba Mountain, Dabie Mountain, Huaihe River Source, Nanling Mountain, Dongjiang River Source, Zoige, Three Gorges Reservoir Area and Danjiangkou Reservoir Area (Figure 2). There are 1,066 nature reserves, including 165 national nature reserves (90 forest ecosystems, 47 wild animals, 14 inland waters, 12 wild plants, 1 geological relic and 1 paleontological relic). The protected area is 1.86×107 hm2, accounting for 9.1% of the total area of the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
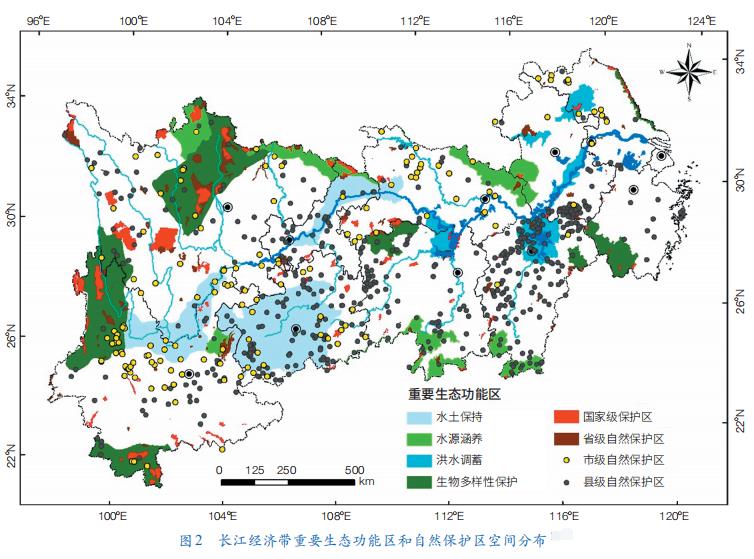
The eco-geographical pattern of economic belt is special, and there are many types of natural ecological disasters with high risk.
The complex and diverse geological and geomorphological environment and special and changeable climatic and hydrological conditions in the Yangtze River Economic Belt lead to frequent natural disasters, mainly floods and mountain disasters. These natural disasters have become a worry of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. The upper reaches of the Yangtze River is located at the junction of the first and second terraces in China, with complex geological conditions, widely distributed alpine and canyon landforms and active neotectonic movements. Earthquakes and landslides and mudslides are not only numerous, widely distributed and large-scale, but also have sudden, mass-produced and disaster chain effects, and major geological and mountain disasters occur almost every year.
The east-west flow direction of the Yangtze River coincides with the direction of the rain belt, which has a long stay time and many persistent rainstorms. The upper reaches of the Yangtze River have a large terrain drop and converge quickly, and the middle and lower reaches have low terrain, so the flood storage and discharge are not smooth, and the upper, middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River often encounter rainstorms and floods. In addition, the river system is developed, and there are many tributaries entering the river, and there are bayonets in the middle reaches of the main stream and tidal supports in the lower reaches of the river, which leads to frequent floods in the Yangtze River, especially in the middle and lower reaches, and the flood disasters are characterized by high peak, large amount and long duration.
Water environment and atmospheric environment are seriously polluted.
The Yangtze River Economic Belt has a long history of development, dense population and relatively developed economy. The rapid industrialization and urbanization process have led to a large total amount of environmental pollutants, and the cumulative effect of environmental pollution is remarkable. The environmental problems marked by the decline of water environment and atmospheric environment quality are prominent. In 2018, 21.1% of the 1,261 important water functional zones failed to meet the standards. From 2006 to 2018, among the 25 state-controlled sections in the main stream of the Yangtze River, the pH value of 9 sections, the dissolved oxygen content (DO) of 12 sections, the permanganate index (CODMn) of 16 sections and the annual average value of ammonia nitrogen concentration of 6 sections showed an upward trend. In 2018, the number of weeks with water quality grade IV and below in seven sections accounted for more than 30% (Figure 3).
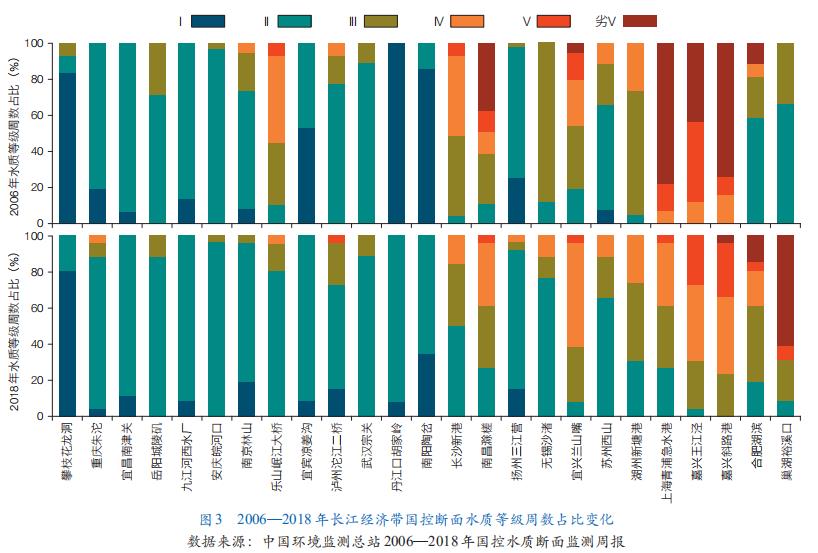
The overall water quality of the lake is poor. Among the 61 major lakes in the Yangtze River Basin in 2018, the water area of Class I-III only accounts for 11.1%, Class IV-V accounts for 86.0%, and Class V is inferior to 2.9%. Poyang Lake, Taihu Lake, Chaohu Lake, Dongting Lake, Dianchi Lake, Wuhan East Lake, Xuanwu Lake, Hangzhou West Lake, etc., except for the overall water quality of Hangzhou West Lake, the water quality of other lakes is IV-worse than V. Of the 108 lakes in the middle and lower reaches with an area of more than 10 km2, 95 (accounting for 88% of the total) exceeded the eutrophication standard, of which 25 (accounting for 23.1% of the total) reached the heavy eutrophication standard, and only 13 (accounting for 12% of the total) were moderately eutrophic and poorly eutrophic lakes.
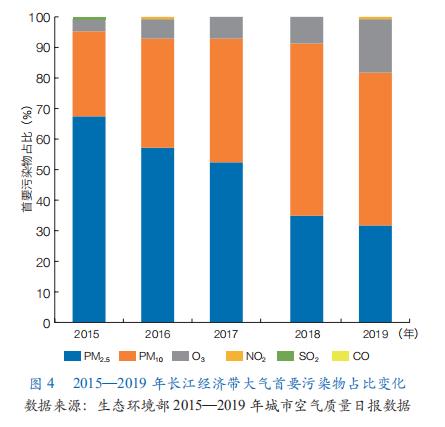
(2) The overall atmospheric environment is worrying. The Yangtze River Delta and Chengdu Plain are among the areas with the highest haze days in China. Among them, most cities in the Yangtze River Delta, Chengdu and its surrounding areas have haze days of more than 50 days, and some cities in Jiangsu and northern Zhejiang have haze days of more than 100 days. Among 126 prefecture-level cities, the average annual concentration of ozone (O3) in 76.2% prefecture-level cities is on the rise, and the average annual concentration of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in 29.4% prefecture-level cities is also on the rise. From 2015 to 2019, the proportion of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the primary air pollutants showed a continuous downward trend, the proportion of inhalable particulate matter (PM10) exceeded 50%, and the proportion of O3 showed a continuous upward trend (Figure 4). Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the Yangtze River Delta are high-value areas in China and even in the world, which causes secondary pollution problems such as O3.
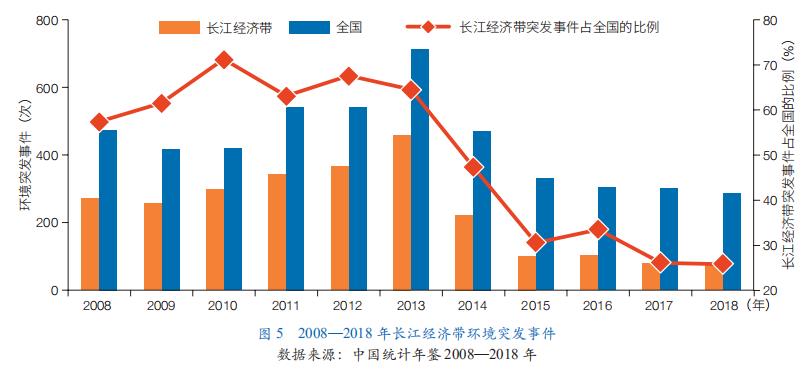
Structural and layout risks are prominent, and sudden environmental incidents occur frequently. There are 62 industrial parks along the Yangtze River, especially heavy chemical enterprises, with more than 250 kinds of hazardous chemicals produced and transported. 40% of papermaking, 43% of synthetic ammonia, 81% of ammonium phosphate, 72% of printing and dyeing cloth and 40% of caustic soda are concentrated in this area, which leads to frequent environmental emergencies and seriously threatens the water supply and ecological security of the local and downstream areas. From 2008 to 2018, there were 2,574 sudden environmental incidents in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, accounting for 53.6% of the national total. Among them, environmental emergencies in Shanghai, Jiangsu and Zhejiang account for more than 80% of the total environmental emergencies in the Yangtze River Economic Belt (Figure 5). After 2013, the sudden environmental pollution incidents in the Yangtze River Economic Belt showed a significant downward trend, but the cumulative and potential environmental risks of high-density layout of heavy chemical enterprises remained high.
The water ecology of the main tributaries and lakes of the Yangtze River has deteriorated significantly.
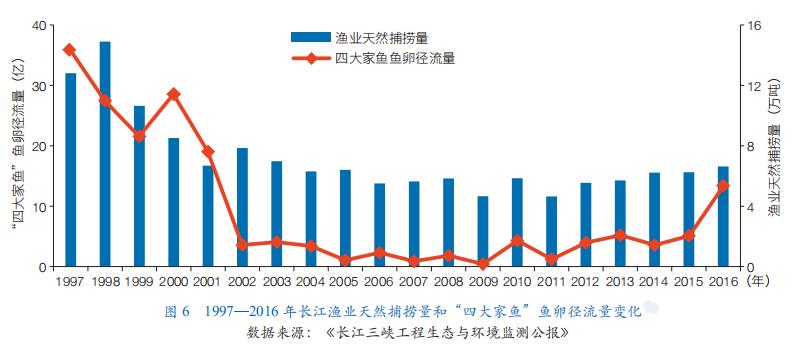
The rapid degradation of aquatic organisms in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, especially a series of cascade hydropower development, has led to the destruction of spawning and breeding grounds and suitable habitats for rare and economic fish to varying degrees. From 2003 to 2010, after the impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir, 23 species of endemic fish were investigated, the number of species decreased by 51.1% compared with that before impoundment, and the dominance of endemic fish in the catch of the Three Gorges Reservoir decreased by 35.3%-99.9%. The spawning scale of "Four Big Fish" decreased significantly. The average annual runoff of "Four Big Fish" eggs in Jianli section of the middle reaches was 228 million, which was 90.0% lower than that in 1997-2002 before impoundment. Although the ecological regulation implemented in 2011 has promoted the improvement trend of the "four big fish", it only accounts for 23.9% from 1997 to 2002 (Figure 6). From 2003 to 2016, the average annual natural fishery catch in the Yangtze River decreased by 42.7% compared with that in 1997-2002. The biological resources of lakes in Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau are degraded, and the indigenous species are rapidly decreasing. The fish fauna evolved from plateau to the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and the indigenous species decreased significantly.
The lake wetland ecology in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River is obviously degraded. The vegetation distribution of Poyang Lake and Dongting Lake beach wetlands in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River is characterized by the succession of area expansion, vegetation belt downward movement and obvious drought, which leads to significant changes in migratory bird habitats. The species and quantity of fish in rivers and lakes are decreasing rapidly, and migratory fish are almost extinct; Large mollusk benthos such as snails and mussels have been greatly reduced, while pollution-resistant water worms and aquatic insects larvae have increased; The population and number of macrocladocera and copepods in zooplankton decreased, while the number of small rotifers and protozoa increased rapidly. The distribution range of aquatic higher plants is greatly reduced, the community composition tends to be simple, large emergent plants disappear along the lake shore, and a large number of lakes change from clear grass lakes to turbid algae lakes.
The cumulative impact of the ecological environment of major projects represented by the disharmony between rivers and lakes is constantly emerging.
The construction of large-scale reservoirs has changed the situation of incoming water and sediment in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, and significantly affected the river and lake water quality, wetland ecology, flood control and water supply safety. In recent decades, all kinds of dam projects in the Yangtze River Economic Belt have grown explosively, and there are more than 20 large-scale controlled water conservancy projects under construction and built in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, represented by the Three Gorges. The construction of large-scale reservoirs has profoundly changed the situation of incoming water and sediment in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, and then has an increasingly obvious impact on the water and ecological environment in the middle and lower reaches. Since 2003, the inflow of the upper reaches of the Yangtze River has been continuously small, and the runoff of Yichang Station in 80% of the years from 2003 to 2014 is less than the average from 1956 to 2014. The inflow in the upper reaches is reduced, and the river channel under the dam in the middle reaches is short of water and sediment. The runoff in Hankou Station in the middle reaches is less than the multi-year average. Since 2003, compared with the average value from 1956 to 2002, the proportion of sediment coming from the upper reaches of Datong station, a control station at the junction of the middle and lower reaches, has dropped sharply from 86% to 37%. On the one hand, the riverbed in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River has been scoured for a long distance and violently. The total scouring amount of the Pingtan river channel from Yichang to Hukou reaches 1.06×109 m3, of which 67% occurs in the Yichang-Chenglingji river channel, and the river channel has been scoured deeply and the bank collapsed from time to time, which seriously endangers the safety of the Yangtze River embankment. On the other hand, it causes the water level in the main stream of the Yangtze River to decrease in different degrees under the same discharge, which leads to the weakening of the Yangtze River’s jacking effect on Tongjiang Lake, and has a far-reaching impact on the lake’s water storage capacity and wetland ecological balance, as well as flood control and water supply safety in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River.
The construction of water conservancy projects and reclamation have intensified the disharmony between rivers and lakes. The Yangtze River Economic Belt is not only the most concentrated area of lakes in China after the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (the number and area of lakes larger than 1 km2 account for 25% of the whole country), but also the most significant change in the number and area of lakes in China in the past century. Historically, most of these lakes were naturally connected with the Yangtze River or other rivers, and they played normal ecological service functions such as flood storage, water purification, fresh water supply and biodiversity maintenance. Since 1950s, the construction of water conservancy projects and reclamation activities, such as man-made dams and dams, have intensified. Most lakes in this area have lost their natural hydraulic connection with rivers, and the relationship between rivers and lakes has gradually become disharmonious.
The barrier between rivers and lakes intensifies lake shrinkage and biodiversity decline. The structure and function of many lake ecosystems have changed due to the sudden change of hydrological and hydrodynamic conditions, and the contact of aquatic organisms between rivers and lakes has been blocked, resulting in the disappearance of migratory aquatic animals from the original distribution areas of rivers and lakes and becoming increasingly endangered, and the species and quantity of aquatic plants in lakes and fish rivers have decreased significantly. Algae, especially cyanobacteria, proliferate in large quantities, and the species of benthos decrease and tend to be miniaturized, which has become an important reason for the frequent occurrence of ecological disasters such as cyanobacteria bloom. For example, in 2007, an outbreak of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake caused a water supply crisis in Wuxi. Intensifying lake shrinkage and reclamation, resulting in a rapid decrease in the number and area of lakes. Since 1950s, the lake area in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River from Yichang to Datong has been reduced from 17 198 km2 to about 6 600 km2, a decrease of about 2/3. The number of lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River with an area of more than 1 km2 accounts for 44.4% of the whole country. The areas of the five major freshwater lakes have all decreased significantly, and the areas of Dongting Lake, Poyang Lake and Taihu Lake have decreased by 1 725 km2, 2 267 km2 and 172 km2 respectively, which directly led to a significant decline in the storage capacity of lakes and a passive situation of minor floods and major disasters.
Major projects are intertwined with the impacts of climate change, which increases the complexity and uncertainty of ecological and environmental problems. Since the beginning of the 21st century, influenced by multiple factors, such as the alternation of dry and wet cycles of climate, the impoundment operation of water conservancy projects in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, such as the Three Gorges Project, and the intensification of human activities in the basin, the hydrological situation of the two existing Tongjiang lakes in Dongting Lake and Poyang Lake has undergone profound changes. The dry season of the lakes is advanced, the dry season is prolonged, and the ultra-low water level occurs frequently, which not only seriously affects the industrial and agricultural production in the lake area and the domestic water consumption of urban and rural residents, but also endangers the ecological balance between lakes and beach wetlands and the habitat degradation of migratory birds, resulting in a series of
Overall protection strategy
The Yangtze River Economic Belt is the region with the best comprehensive development conditions in China. It has a superior location with moderate north-south and east-west connectivity, a unique ratio of water, soil, gas and natural resources, and a relatively complete industrial and urban system. "Great protection and no great development" is not just protection and no development, but protection should be given priority and prominence. We should not take the old road of extensive and disorderly development at the expense of ecology and environment. We must take "great protection" as the premise, develop scientifically, orderly and intensively according to local conditions, and take the road of ecological civilization development in which man and nature coexist harmoniously.
Put the protection of water ecological environment in the Yangtze River in the first place and take the lead in implementing water quality target management.
Strengthen the management and control of the development of industries and parks along the Yangtze River and implement the source control of pollutants entering the river. Take the management of the occupation of the Yangtze River coastline as the core of regulating the orderly development along the Yangtze River, include the coastline land depth of 0.5—1 km and the bund land in the coastline category, follow the principles of ecological priority, intensive development and paid use, and implement the occupation permit system of the Yangtze River coastline. Strictly manage the scattered layout of industrial enterprises along the Yangtze River and the establishment of heavy chemical industrial parks, clean up and shut down polluting enterprises outside the parks within a time limit, and change the situation that heavy chemical industries along the Yangtze River are scattered, and pollution and risks are difficult to control. For all kinds of development zones and industrial parks set up along the Yangtze River, it is mandatory to build high-standard and full-coverage sewage treatment systems, standardize and strictly control the setting of sewage outlets along the Yangtze River, ensure that there is no scattered industrial and domestic sewage to be discharged directly, and prohibit water bodies whose tributaries fail to meet the Class V standard from entering the Yangtze River; In addition, regional environmental protection measures should be implemented for the coastal sections that cannot meet the basic requirements.
Strengthen the target management of water quality in the main tributaries and key lakes of the Yangtze River. Actively explore the target management mode of river basin environmental quality, and take the lead in realizing the transformation of environmental management in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from pollution reduction target assessment to environmental quality target assessment.
Form a pattern of land space development and protection that is economical and intensive in development and ecological and natural openness.
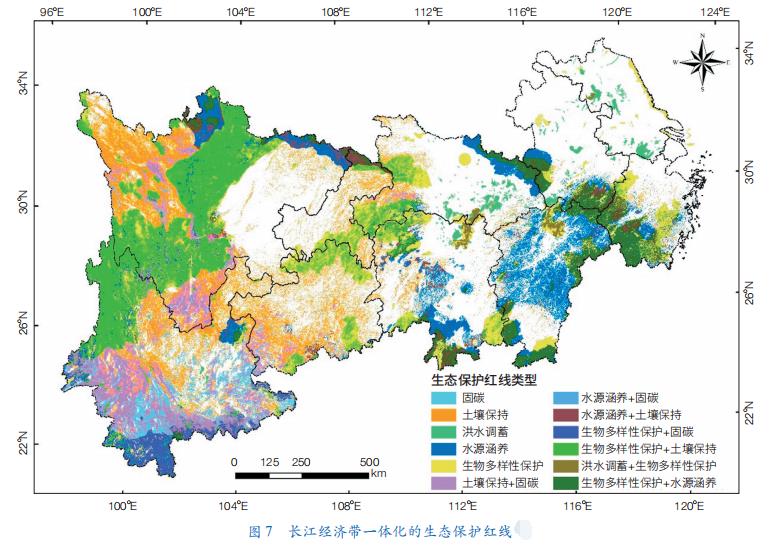
Strengthen the protection of ecosystem integrity and connectivity. Focus on maintaining ecosystem services in important ecological functional areas and controlling the development intensity of ecologically sensitive (fragile) areas, optimize the delineation of ecological protection red line (Figure 7), effectively control the development scale and order of hydropower projects, strengthen ecological nature conservation and river-lake connectivity, and build a land-water composite ecological corridor with the Yangtze River as the main axis.
Strengthen the ecological guidance of land development and optimize the layout of spatial development. Combined with the control of shoreline occupation, the ecological, living and production spaces are reasonably delineated, and various space environment access thresholds are formulated and negative lists are developed. We will implement strict ecological red line control and environmental damage compensation system, strengthen centralized and intensive development of important urban agglomerations and provincial and above development zones, and protect agricultural development space and green open space. Accelerate the formation of a new pattern of land and space development, in which centralized and intensive development and ecological openness complement each other and the main functions of the region are clear.
Continue to implement the green ecological security project in the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
Implement the water security project. Strengthen the protection of water conservation areas by focusing on the protection of the source and upper reaches of the Yangtze River, the rational allocation of water in the middle reaches and the protection of the downstream water environment; Delineate the red line of river and lake protection to ensure that the area of rivers and lakes does not decrease and the storage capacity does not decrease; Carry out returning farmland to lakes and wetlands, prohibit illegal occupation of rivers, lakes and beaches, limit the development intensity of flood storage and detention areas, and restore and increase the water resources storage capacity; Strengthen the unified management and optimal operation of the main and tributary reservoirs, implement the connection between rivers and lakes, clean water into rivers and clean small watersheds, and effectively ensure regional water security.
Implement natural ecological conservation projects. Strengthen the water ecological protection focusing on the protection of fish resources in the Yangtze River, strictly control the reclamation and development of wetlands in the Yangtze River, and carry out ecological dispatching of water conservancy projects conducive to fish protection, so as to effectively protect biodiversity and the health of the Yangtze River water ecosystem.
Implement major disaster prevention projects. Delineate the risk areas of mountain disasters such as earthquakes, landslides and mudslides in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, and implement the project of resettlement and town construction in high-risk areas; Increase the construction of ecological projects such as returning farmland to forests and grasslands on steep slopes, greening barren hills and hills, and continuously slow down the harm of soil erosion; The comprehensive flood control system of the Yangtze River is formed by organically combining the dike reinforcement of the Yangtze River and its main tributaries with the construction of flood storage and detention areas and the joint optimal operation of reservoirs in the main tributaries of the Yangtze River.
Implement environmental and ecological risk prevention projects. Establish a negative list, and build a strict system of classified supervision of environmental and ecological risk sources and real-time risk monitoring, early warning and disposal; Promote environmental information sharing and build a regional joint prevention and control and emergency response mechanism; Strictly control the layout of polluting enterprises in sensitive coastal areas and regions and the transportation of hazardous chemicals.
Breaking the division between departments and localities and implementing integrated river basin management
Break the division between departments and localities, and set up an inter-departmental and inter-administrative Yangtze River basin management institution directly under the State Council. Draw lessons from the management experience of Rhine River in Europe and Tennessee River in the United States, and establish a comprehensive management mechanism for the Yangtze River basin through consultation and decision-making by stakeholders; Efforts will be made to solve cross-regional and cross-departmental problems that cannot be solved within various administrative units and departments, coordinate the preparation of comprehensive river basin planning and integrated control of spatial development, and supervise the implementation of the Yangtze River Protection Law.
Establish and improve the system of natural resources protection and management, environmental damage compensation and responsibility investigation and ecological compensation in the whole Yangtze River basin. In accordance with the general requirements of "adhering to and improving the system of ecological civilization system and promoting the harmonious coexistence between man and nature", we will take the lead in establishing and improving the property right registration of natural resources assets, the paid use of natural resources such as hydropower, minerals and water, the total resource management, and the matching asset profit and loss evaluation and assessment mechanism; Change the phenomenon of "enterprises make money, the government pays the bill, and the people suffer" in environmental damage, establish a mechanism for compensation and compulsory repair of environmental damage, and investigate the responsibility for environmental damage reasonably and legally; Based on the benchmark value of key water quantity and water quality indicators of control section agreed by the state-controlled or stakeholders, the ecological compensation, paid use of natural resources and environmental damage compensation system are combined, and according to the difference between the key indicators and the benchmark value, a two-way compensation (compensation) mechanism for upstream and downstream of the basin is established and improved. (Author: Yang Guishan, researcher of Nanjing Institute of Geography and Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, president of Nanjing Branch of China Academy of Sciences; Xu Xibao, Nanjing Institute of Geography and Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Contributed by Journal of China Academy of Sciences)