Secretly open sensitive permissions Xiaomi Huawei "audit on behalf of users"?
The reporter downloaded a variety of APP tests, and different mobile phones have different privacy rights. When downloading, Huawei and Xiaomi App Stores open multiple sensitive rights by default.
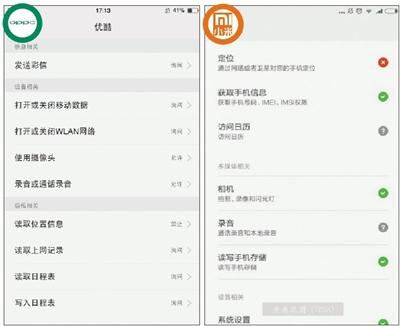
Download the permissions opened when you open Youku in the OPPO (left) and Xiaomi (right) mobile app stores for the first time. Image source: Beijing News
The Beijing News reporter previously investigated and tested various apps and found that under the Android system, many commonly used apps collected sensitive information without explicit reminders. Recently, the reporter further investigated and found that the same APP has different behaviors of reading sensitive information under the Android system of different brands of mobile phones.
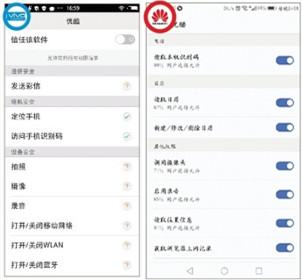
Download the permissions opened when you open Youku for the first time in the mobile app stores of vivo (left) and Huawei (right). Image source: Beijing News
From January 24th to February 8th, the Beijing News reporter found that seven APPs, Tmall, Ctrip, 58 Tongcheng, Youku, Today Headline, Iqiyi and Jiji.com, were downloaded from the built-in APP stores of Huawei, Xiaomi, OPPO and vivo, and their location or other sensitive permissions were turned on by default without explicit reminders, while their permissions were basically explicitly reminded when they were downloaded from the OPPO and vivo app stores.
"When downloading a normal APP, there will be operations to grant permissions. If an individual APP does not, it can only show that it has something to do with the application market built into the mobile phone." Li Yu (pseudonym), who is engaged in the development of Android system, told reporters, "In fact, when the APP is on the white list of mobile phone manufacturers, it is possible for the app store to omit the operation of prompting permissions for users."
Dr. Ma Zhaofeng, director of the Joint Laboratory of Mobile Internet and Big Data Security of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, once said that some APP product manufacturers and software stores have cooperated to release the right of choice that should prompt users to know in a white list mode, so there is no prompt for "express consent". This does not meet the norms and requirements for the safe use of personal information.
Huawei Xiaomi Store has incomplete privacy tips for many apps.
According to Article 41 of the Cyber Security Law, when collecting and using personal information, network operators should follow the principles of legality, justness and necessity, make public the rules of collection and use, clearly state the purpose, manner and scope of collection and use of information, and obtain the consent of the collected person.
The Information Security Technology Personal Information Security Specification issued by China National Standardization Administration Committee (hereinafter referred to as the Specification) defines personal sensitive information and clarifies the principles of collecting information. One of the most important ones is the principle of "optional consent", that is, the APP party needs to clearly indicate the purpose, method and scope of information processing to the subject of personal information and ask for its authorization and consent. The specification was officially implemented on May 1, 2018.
The Code points out that when collecting sensitive personal information, the express consent of the subject of personal information should be obtained. Express consent refers to the behavior that the subject of personal information makes a clear authorization for specific processing of his personal information through a written statement or active affirmative action.
"During the use of the APP, the user clicked agree when he saw the permission request pop-up, which is a positive action." Li Yu said, "Specifically, affirmative actions include the user’s initiative to make a statement (electronic or paper form), take the initiative to check, take the initiative to click agree, register, send, dial, etc."
However, at present, not all apps on the market have explicitly reminded the required permissions according to regulations. Previously, Jiangsu Consumer Protection Committee had filed a civil lawsuit against Baidu on the grounds that mobile phone applications infringed consumers’ personal information and there was no rectification in two interviews. Tian Biao, senior manager of mobile phone Baidu, previously responded that some systems will grant some permissions to APPs that it thinks are safe. The authorization of Android system is very complicated, and the authorization depends entirely on the mobile phone system itself, not judged and decided by the app itself.
In order to verify whether the authorization will change due to the differences in mobile phone systems, from January 24th to February 8th, the Beijing News reporter installed the same eleven apps on Huawei, Xiaomi, OPPO and vivo Android phones. The eleven apps are Tmall, Ctrip, Baidu Map, Tencent Video, Baidu, JD.COM, 58 City, Today Headline, Youku, iQiyi and Jiji.com..
The test results show that the same APP has different explicit reminders when it is downloaded in different brands of mobile phone application markets. Among them, some apps explicitly reminded sensitive permissions after the installation of vivo and OPPO mobile phones, but did not explicitly remind sensitive permissions after the installation of Huawei and Xiaomi mobile phones.
Among them, four apps, Baidu, Baidu Map, JD.COM and Tencent Video, will clearly remind users when the above four brands of mobile phones are downloaded and opened for the first time, while the permissions of the other seven apps will produce different results according to different mobile phone brands.
Take Tmall as an example. When the reporter downloaded the APP through the built-in app stores of Huawei, Xiaomi and OPPO phones, it was found that there was no explicit reminder when it was first installed and used. However, through the permission setting in the background, it was found that Tmall was installed in Xiaomi mobile phone. After that, the positioning, camera and recording permissions were turned on by default; After the installation of Huawei mobile phone, the permissions of positioning, camera and reading call records are turned on by default; After the installation of OPPO mobile phone, no permissions have been opened; After the installation of vivo mobile phone, it clearly reminds and opens the location permission.
The reporter’s test found that seven APPs, Tmall, Ctrip, 58 Tongcheng, Youku, Iqiyi, Today Headline and Jiji.com, were downloaded in Huawei and Xiaomi’s mobile phone built-in APP stores without explicit reminders. When downloading in vivo and OPPO mobile phone built-in app stores, all the other apps were explicitly reminded, except Youku, which turned on the camera and recording by default when installing OPPO.
From the above examples, among the 11 apps, 4 apps including Baidu and JD.COM have made explicit reminders of all sensitive permissions in Xiaomi and Huawei, 10 apps have made explicit reminders of all sensitive permissions in OPPO, and 11 apps have made explicit reminders of all sensitive permissions in vivo.
Mobile APP store "reviews" app permissions on behalf of "users"
"The reason for the different requests for APP rights on different mobile phone brands is that the review strategies of online apps in each mobile phone brand application market are different." Li Yu said, "As an APP party, we must honestly apply for permission, and then make changes according to the requirements of business review in the application market."
On February 6th, the Beijing News reporter contacted the relevant person in charge of the audit in Huawei APPlication market as a developer, and wanted to know whether his app could be put on Huawei application market by default. The answer is, "Whether the permission is turned on by default or not, developers can’ realize it by themselves’ in their own SDK (software development kit)." However, the person also said that if the application request authority is too high, there may be situations such as reading the user’s call record, reading the user’s address book, reading the user’s short message record, obtaining the user’s mobile phone number, and pushing advertisements in the notification bar, which does not meet Huawei’s application market audit standards.
"The application market generally implements the minimum permission policy unless the permission is just needed. For example, reading the address book is to add friends to the address book." Li Yu explained, "As for the specific permissions that the APP can open, it depends on the review requirements of the app store. If the app store feels that the permission you requested is for a proper purpose, it can be put on the shelves. As for the function of opening the permission by default, it can only be related to the app store. "
It should be noted that the app store itself has the audit function. For example, the Xiaomi App Store Application Audit Specification clearly stipulates that the application shall not collect, transmit or use the user’s location information without prompting the user or without the user’s authorization. The "OPPO Application Market Audit Rules" also stipulates that users’ location information shall not be collected, transmitted or used without the authorization of users.
According to the "Huawei Application Market 2017 Safety Report" released by Huawei, the Huawei application market accepted 647,000 applications for putting applications on the shelves in 2017, of which 202,000 failed the audit, with a passing rate of 68.8%. Among the apps that failed the audit, 15.4% failed because Huawei judged that there was "malicious behavior".
"Downloading the APP from the app store itself must undergo security monitoring, which is good for users’ privacy protection. However, mobile phone manufacturers have given the built-in application market a higher authority, thus bypassing the authority prompt of the original Android system, which itself violates the principle of choice and consent in the Specification and does not comply with relevant regulations." Li Yu said.
On February 5, the reporter downloaded the Tmall APP installation package on Huawei’s mobile phone using a browser and found that during the installation process, the requested authority was clearly stated. But when you use the app store to download, the explicit reminder disappears.
"When downloading through the browser, all the permission tips are listed above. If you install it in the app store, it will omit this process for you. Because the app store itself is built into this system, its authority is called vendor authority, which is basically as high as root’s authority, so it has the ability to do these things. " Fang Ning, vice president of Bangbang Security R&D Center, explained.
In Fang Ning’s view, the original system and the APP downloaded from the APP market all use the same program, but when users download the APP through the built-in app store of mobile phones, the app store is dominant and has the right to speak, and the app party must pass the review of the app store before putting its own app on the shelves. "This is different from other mobile phone manufacturers. Because Apple’s operating system can’t be customized like Android, there will be no problem of vendor permissions."
Different brands of mobile phones have different judgments on privacy rights.
The Beijing News reporter found that different mobile phone brands have different judgments on privacy rights.
For example, when downloading iQiyi from Xiaomi and Huawei’s built-in app stores, although there is no explicit reminder, from the background permission system, it can be found that Xiaomi’s mobile phone has turned off the call permission of iQiyi, but has turned on the location and recording permission; Huawei, on the other hand, closed the right to locate and record, but it was just "lenient" with the right to make calls.
Tencent video has clearly stated the privacy agreement on all four brands of mobile phones, which also means that Tencent video can open privacy rights legally. However, the reporter checked the background permission system and found that Tencent Video did not open any privacy permission on Huawei and Xiaomi mobile phones, but opened the camera and recording permission on OPPO mobile phones.
In this regard, a technician responsible for the development and customization of an APP told the Beijing News reporter that although mobile phones are all Android, they are not Google’s pure original system. Because different mobile phone manufacturers have different concepts on user experience and product design, each mobile phone manufacturer will make some own optimizations for their own systems. For example, OPPO may not set the default usage for some permissions, while other brands of mobile phones may pass by default. On the other hand, according to the prototype and product requirements, developers can also set no pop-up prompts in software design, but there will be different rules when different APPlication stores are put on the shelves, which may also affect the expression of the final permissions of the app.
However, according to Li Tiejun, a cheetah security expert, the "optimization" of Android system by manufacturers will not change much from the cost perspective. Because "the bigger the change, the more expensive the subsequent version upgrade."
In fact, the game between mobile phone manufacturers and apps on user privacy data has already begun.
In August 2017, Huawei and Tencent had a dispute over the use of user data. The cause of the incident is the highly recognized user scene featured by Huawei’s glory Magic mobile phone. For example, when the words "watching movies" are mentioned in the chat process, the mobile phone will automatically give the current popular movie recommendation, and further recommend nearby cinemas and even choose seats to buy tickets.
However, the realization of this technology requires corresponding data analysis, so Tencent accused Huawei of "obtaining Tencent’s data and infringing the privacy of WeChat users."
In this regard, Ding Ke, vice president of Tencent, once said in an interview with the Beijing News reporter that the value orientation of WeChat never involves users chatting with each other, and Huawei’s AI technology can be more efficient, but the concepts of the two companies are really different.
Ms. Ren, who works in Beijing, uses Huawei mate 10 mobile phone. She found that the "smart life" reminder page of the mobile phone can display her train ticket reservation information, express logistics information, and even accurately display her parking information one day. "I am surprised, why can the mobile phone know that I have a car and know where my car is parked?"
In this regard, Li Tiejun, a cheetah security expert, said that in order to realize related functions, mobile phone manufacturers can specially set their own official applications, and then open access interfaces to these official applications. In this way, booking information, express delivery information, etc. can be used to query the services related to users’ lives through the data query interface of the corresponding manufacturers.
Beijing News reporter Luo Yidan
|
|